
29 Jun How Experiential Education can Improve Learning Experiences
With teaching methodologies changing due to the implementation of technology, it can be overwhelming when browsing, which way is truly the best way to teach students. However, it comes down to this one simple answer: It depends. A new school of thought gaining in popularity is based on experiential learning.
A simple definition of experiential education – is learning by doing. Furthermore, it is becoming more mainstream due to disengagement being a major problem in educational institutions. For instance, most of the time during lectures, there is minimal to no participation during the lesson and is solely focused on memorization. An ongoing challenge has been with the current education model, accusing that the content learned is not suitable in the real world and doesn’t translate into careers or endeavours.
| Conventional Learning | Experiential Learning |
| Theoretical Based | Focused on Individual Growth |
| The Transfer of Knowledge | Hands-on Activities |
| A Fixed Mindset | A Growth/Flexible Mindset |
| Ex: slide-deck presentations, lectures | Ex: Hobbies, Passion Projects |
The philosophy of experiential education was promoted by John Dewey, an educator and philosopher in the early 20th century along with others during the progressive movement in education. This philosophy emphasizes the importance of focusing on the whole person in education including one’s physical, emotional and intellectual growth. Additionally, learners are encouraged by educators to experiment and think independently with support and guidance.
The University of Colorado suggests 4 elements that make an activity qualify as experiential learning:
- Reflection, critical analysis, and synthesis
- Opportunities for students to take initiative, make decisions, and be accountable for the results
- Opportunities for students to engage intellectually, creatively, emotionally, socially, or physically
- A designed learning experience that includes the possibility to learn from natural consequences, mistakes, and successes
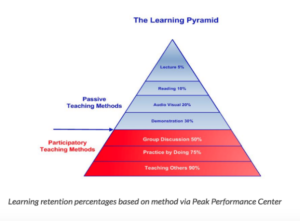
According to The Peak Performance Center, experiential learning creates a bridge between learning the theory and practicing the theory, which leads to a higher rate of learning retention. Furthermore, Sousa and Willis’ studies of the brain and learning are showing that physical, emotional and social involvement in learning increases engagement and retention.
By developing people as individuals, it is not simply transferring arbitrary capabilities, but it helps develop essential things such as confidence, self-esteem, personal strengths and essentially a sense of purpose and fulfillment. Ultimately, this leads to an improved attitude, life-balance, and emotional well-being. These elements are just as important for a productive and healthy workforce as conventional qualities.
At Prepr, we align our objectives with the framework of experiential education. We promote a growth and flexible mindset along with a combination of hands-on activities as it is important to adapt and adjust to the changes around us.
Learn More About Prepr Here.
